What are the general requirements for reinforcement connection in construction engineering?
Reinforcement connection methods can be divided into binding, overlapping, welding, mechanical connection, etc. Since the force transmission performance of the reinforcement through the connection joint is not as good as that of the whole reinforcement, the reinforcement connection principle is as follows: the reinforcement joint should be set at the place with less stress, less joints should be set on the same air root reinforcement, and the longitudinal stressed reinforcement joints in the same member should be staggered from each other.
1. Regulations on joint use
(1) For reinforcement with a diameter greater than 12mm, welded joints or mechanical joints shall be preferred.
(2) When the diameter of tensile reinforcement is greater than 28mm and the diameter of compression reinforcement is greater than 32mm, binding lap joint shall not be used.
(3) The longitudinal stressed reinforcement of axial tension and small eccentric tension rod parts (such as the tie rod of truss and arch) shall not adopt binding lap joint.
(4) In structural members directly bearing dynamic load, the longitudinal tensile reinforcement shall not adopt binding lap joint.
2. Allowable percentage of joint area
In the same connection section, the percentage of overlapping joint area of longitudinal reinforcement is the ratio of the cross-sectional area of longitudinal stressed reinforcement with overlapping joint in this section to the cross-sectional area of all longitudinal stressed reinforcement.
(1) The length of the connection section of the reinforcement binding lap joint is 1.3l1 (L1 is the lap length). All lap joints with the midpoint of the lap joint within the length of the connection section belong to the same connection section (Fig. 9-8). In the same connection section, the area percentage of lap joint of longitudinal tensile reinforcement shall meet the design requirements; When there are no specific requirements in the design, the following provisions shall be met:
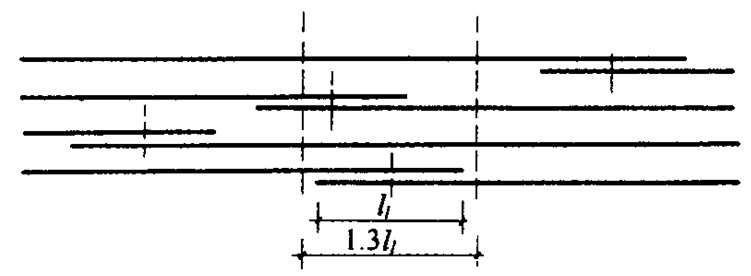
Binding lap joint of longitudinal tensile reinforcement in grounding section
1) For beam, plate and wall components, it shall not be greater than 25%;
2) For column components, it should not be greater than 50%;
3)When it is necessary to increase the percentage of joint area in the project, it shall not be greater than 50% for beam members; For other components, it can be relaxed according to the actual situation.
The area percentage of lap joint of longitudinal compression reinforcement shall not be greater than 50%.
(2) The length of the connection section between mechanical connection of reinforcement and welded joint is 35 times d (D is the larger diameter of longitudinal stressed reinforcement), and shall not be less than 500mm. In the same connection section, the joint area percentage of longitudinal stressed reinforcement shall meet the design requirements; When there are no specific requirements in the design, the following provisions shall be met:
1) The tensile area shall not be greater than 50%; The pressure area is not limited;
2) The joint should not be set in the stirrup densification area at the beam end and column end of the frame with seismic fortification requirements; When it is impossible to avoid, the mechanical connection joint with equal strength and high quality shall not be greater than 50%;
3) Welded joints should not be used in structural members directly bearing dynamic loads; When mechanical connection joint is adopted, it shall not be greater than 50%.
3. Lap length of binding joint
(1) The lap length of the binding lap joint of longitudinal tensile reinforcement shall be calculated according to the percentage of the area of the reinforcement lap joint located in the same connection section according to the following formula:
ll=ξla
Where La anchorage length of longitudinal tensile reinforcement
ξ Correction factor for lap length of longitudinal tensile reinforcement
Correction factor for lap length of longitudinal tensile reinforcement
|
Percentage of lap joint area of longitudinal reinforcement(%) |
≤25 |
50 |
100 |
|
ξ |
1.2 |
1.4 |
1.6 |
(2) When the longitudinal compression reinforcement in the member is connected by overlapping, the compression overlapping length shall not be less than 0.7 times of the overlapping length of the longitudinal tensile reinforcement, and shall not be less than 200mm in any case.
(3) Within the overlapping length of longitudinal stressed reinforcement of beam and column components, stirrups shall be configured according to the design requirements. When there are no specific requirements in the design, the following provisions shall be met:
1) The diameter of stirrup shall not be less than 0.25 times of the larger diameter of overlapping reinforcement;
2) The stirrup spacing in the tensile overlapping section shall not be greater than 5 times the smaller diameter of the overlapping reinforcement, and shall not be greater than 100mm;
3) The spacing of stirrups in the compression overlapping section shall not be greater than 10 times the smaller diameter of the overlapping reinforcement, and shall not be greater than 200mm;
4) When the diameter of the longitudinal stressed reinforcement in the column is greater than 25mm, two stirrups shall be set within l00mm outside the two end faces of the lap joint, and the distance between them should be 50mm.
 五隆兴科技发展有限公司
五隆兴科技发展有限公司




